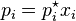Relation between Raoult’s Law and Dalton’s Law :-
If the mole fractions of solute(A) and solvent(B) in liquid phase are XA and XB , and their vapour pressures in pure state are P0A and P0B respectively. Vapour pressure of the solution is P.
If the mole fractions of solute and solvent in Vapour Phase are YA and YB respectively than-
According to Raoult’s Law PA = P0A . XA
And according to Dalton’s Law PA = YA . P
Then P0A . XA = YA . P and P0B . XB = YB . P
ð YA = (P0A . XA )/P , similarly for B YB = (P0B . XB )/P
Now using XA + XB = 1
Substituting XA and XB,
(YA .P) / P0A + (YB .P) / P0B = 1
ð YA/P0A + YB/P0B = 1/P